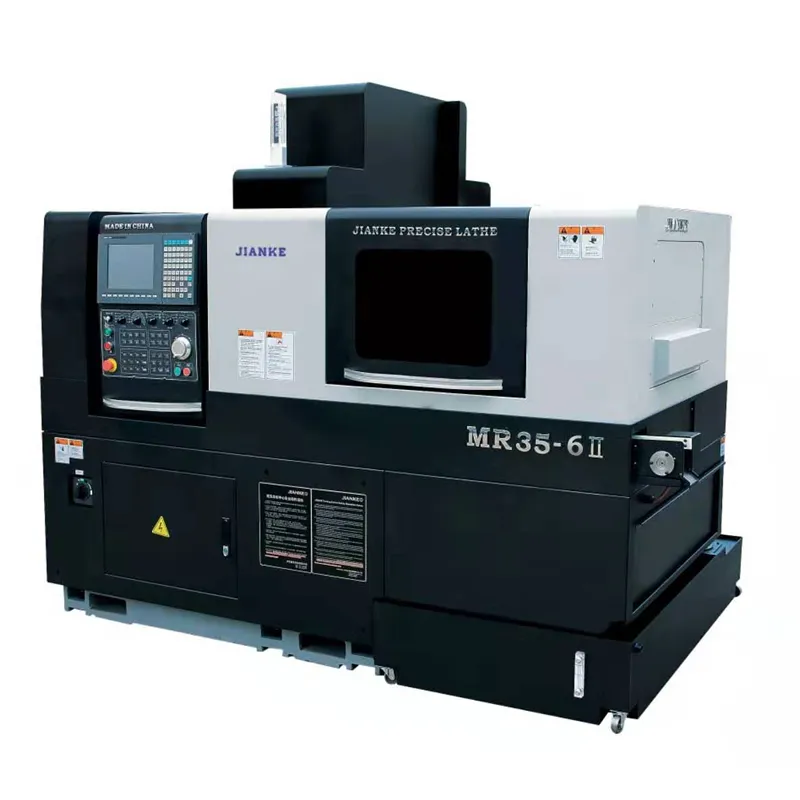
In the world of precision machining, two types of lathes stand out for their distinct capabilities: the Swiss Type Lathe and the traditional lathe. Both are designed to cater to different manufacturing needs, making them essential tools in various industries. The Swiss Type Lathe is renowned for its precision and efficiency in producing small, complex parts, making it a staple in sectors like aerospace, medical devices, and automotive. In contrast, traditional lathes are better suited for larger and simpler components, often used in general machinery parts. This article delves into the design, functionality, and application differences between these two types of lathes, highlighting their unique strengths and weaknesses.
Design Differences
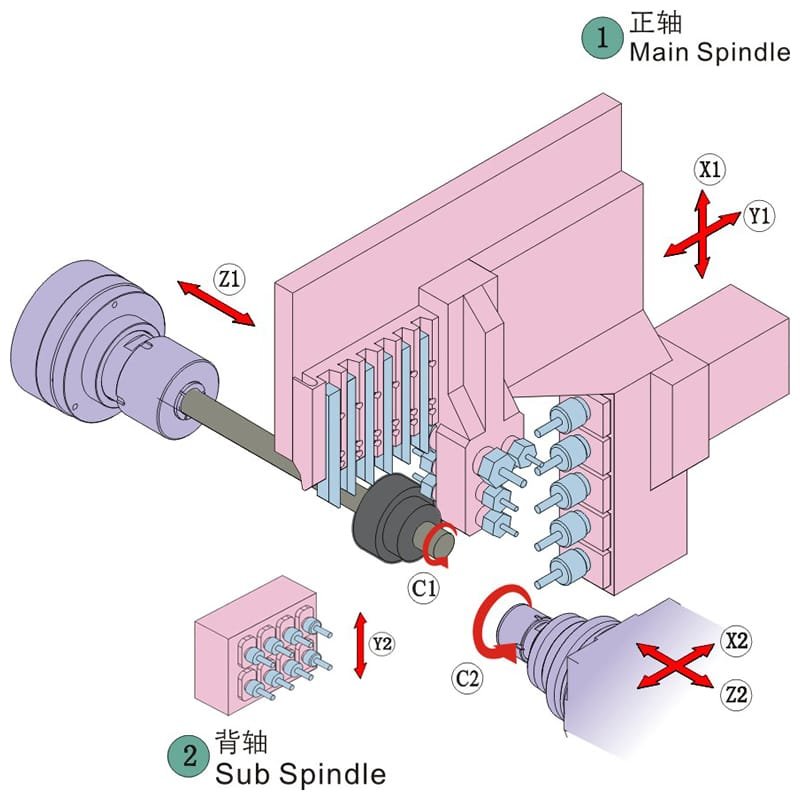
Swiss Type Lathe
The Swiss Type Lathe is distinguished by its innovative design features that enable precise machining:
- Movable Headstock and Guide Bushing: The movable headstock allows for flexible machining operations, while the guide bushing ensures that bar stock is precisely guided through the machine, reducing vibration and enhancing accuracy. This setup is particularly beneficial for producing long, thin parts with high precision.
- Precision Machining Support: Optimized for small, complex parts, the Swiss Type Lathe integrates multiple tools and operations in a single setup, ideal for manufacturing intricate components.
Traditional Lathe
Traditional lathes have a more straightforward design:
- Fixed Headstock: With a fixed headstock, traditional lathes offer less flexibility in machining compared to the Swiss Type Lathe. This design is more suited for larger parts where precision is not as critical.
- No Guide Bushing: Without a guide bushing, traditional lathes rely on manual material alignment and feeding, which can lead to variations in quality and efficiency.
Functional Differences
Swiss Type Lathe
The Swiss Type Lathe offers several functional advantages:
- Continuous Machining Capability: Equipped with a bar feeder, it can continuously process parts without manual intervention, significantly increasing production efficiency. This feature is invaluable in high-volume manufacturing environments.
- High-Speed Spindle and Quick Tool Change: The high-speed spindle enables faster machining operations, while the quick tool change system minimizes downtime between operations. These features are crucial for maintaining high productivity levels.
- Multi-Axis Capability: Typically featuring five or more axes, the Swiss Type Lathe can perform complex machining tasks in a single setup. This capability reduces the need for secondary operations and enhances overall precision.
Traditional Lathe
Traditional lathes have more limited functionality:
- Manual Material Loading: Traditional lathes require manual loading of materials, which can be time-consuming and less efficient compared to automated systems.
- Fewer Axes: Typically featuring three to four axes, traditional lathes are better suited for simple machining tasks and may require additional setups for complex parts.
Application Differences
Swiss Type Lathe
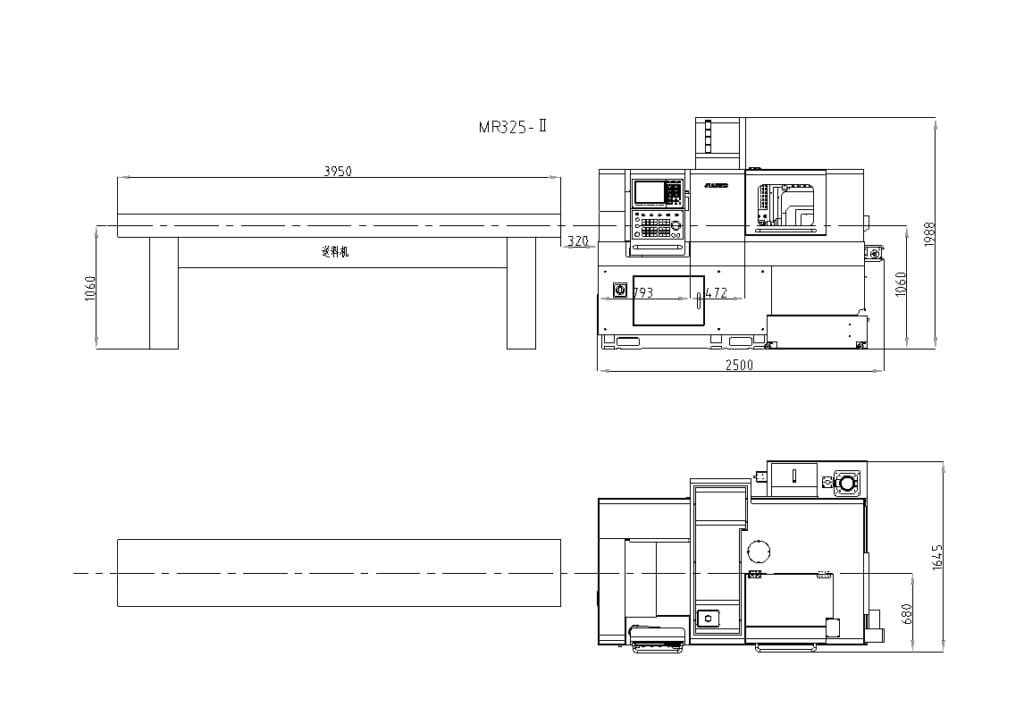
The Swiss Type Lathe MR35-6 is widely used in industries where precision and complexity are paramount:
- Aerospace, Medical, and Automotive Industries: These sectors benefit from the Swiss Type Lathe’s ability to produce intricate, high-precision parts. Its capability to maintain tight tolerances and handle long, thin parts makes it ideal for manufacturing components such as aircraft parts, medical implants, and automotive components.
- Long and Thin Parts: The Swiss machine tools excels at producing parts with high length-to-diameter ratios, ensuring consistent quality and precision throughout the entire length of the part.
Traditional Lathe
Traditional lathes are more commonly used for simpler applications:
- General Machinery Parts: They are well-suited for manufacturing larger, less complex parts such as gears, shafts, and other general machinery components.
- Traditional Manufacturing: In some traditional manufacturing settings, the simplicity and lower cost of traditional lathes make them a viable choice for producing straightforward parts.
Cost and Return on Investment Analysis
Swiss Type Lathe
While the Swiss Type Lathe requires a significant initial investment, it offers substantial long-term benefits:
- High Initial Cost: The purchase price of a Swiss machine tools is typically higher due to its advanced technology and precision capabilities.
- High Production Efficiency and Precision: The ability to produce parts quickly and accurately leads to increased productivity and reduced waste. This efficiency can result in lower long-term costs and higher profitability, especially in high-volume production environments.
Traditional Lathe
Traditional lathe offer a more affordable entry point but may have higher operational costs over time:
- Lower Initial Cost: The initial investment for a traditional lathe is generally lower, making it more accessible to smaller operations or those with limited budgets.
- Lower Efficiency and Precision: While the upfront cost is lower, traditional lathes may require more labor and time to produce parts, potentially leading to higher operational costs over time due to inefficiencies and lower precision.
—
In conclusion, the Swiss Type Lathe and traditional lathe serve distinct roles in the manufacturing sector. The Swiss machine tools excels in precision, efficiency, and complexity, making it ideal for industries requiring high-precision parts. Despite its higher initial cost, the long-term benefits of increased productivity and precision can justify the investment for many manufacturers. On the other hand, traditional lathes remain suitable for simpler applications where cost is a primary concern. Understanding these differences is crucial for manufacturers to choose the right tool for their specific needs, ensuring optimal production outcomes and cost-effectiveness.





