Have you ever wondered how those complex surfaces and precision parts in modern industry are manufactured so efficiently? The answer often lies in the use of 5-axis CNC machine. Compared to traditional 3-axis machine, 5-axis CNC machine can process workpieces from more angles, dramatically improving efficiency and precision. Whether it’s an aerospace turbine blade or a complex automotive mold, 5-axis CNC machine play an irreplaceable role.
Today, let’s dive into the fundamentals of 5-axis CNC machine. From their definition and working principles to their various types and application fields, this article will help you fully understand this advanced manufacturing technology. Whether you’re new to the industry or a business owner considering equipment upgrades, you’ll find practical insights and inspiration here.
What Is a 5-Axis CNC Machine?
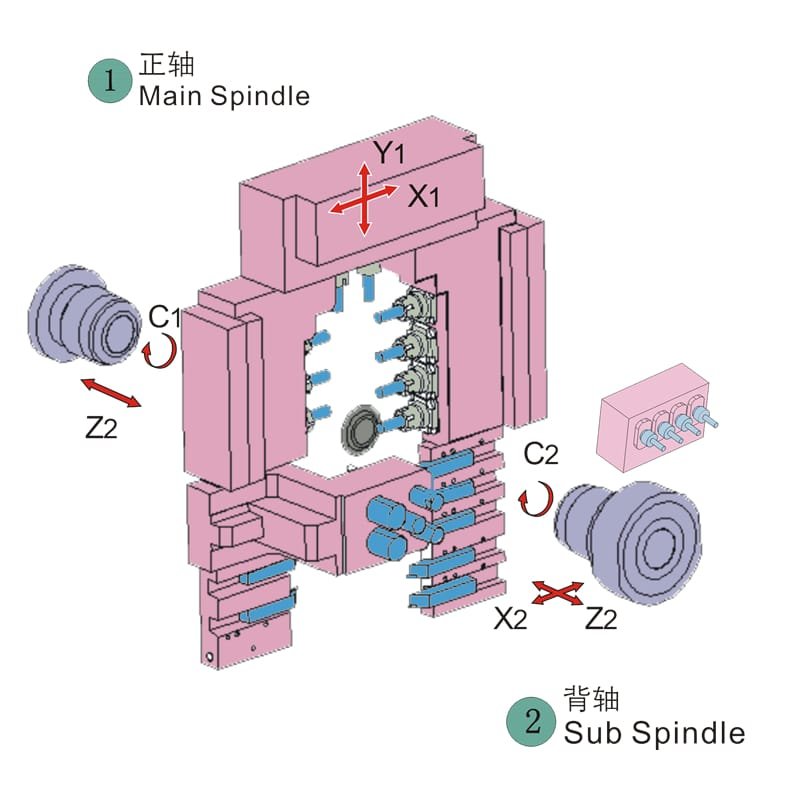
Put simply, a 5-axis CNC machine is a numerically controlled machine tool capable of moving in five different directions simultaneously. The “5 axes” refer to three linear axes (X, Y, Z) plus two rotational axes (commonly called A and B or C axes), allowing the tool to approach the workpiece from many more angles.
Differences Between 3-Axis, 4-Axis, and 5-Axis Machines
| Machine Type | Number of Axes | Degrees of Freedom | Machining Capability | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-Axis | 3 | X, Y, Z | Simple flat and linear machining | Basic parts |
| 4-Axis | 4 | X, Y, Z + rotation | Simple curved and ring machining | Some complex parts |
| 5-Axis | 5 | X, Y, Z + 2 rotations | Complex surfaces, multi-face machining | High-precision, complex parts |
Basic Structure of a 5-Axis CNC Machine includes the bed, spindle, tool holder, CNC system, and five motion axes. Each component works together to ensure efficient and precise machining.
Working Principle
You might ask, “How do 5-axis machines actually move?” The secret lies in the coordinated motion of all five axes.
- Three linear axes (X, Y, Z): Responsible for straight-line movement of the tool or workpiece.
- Two rotational axes (A, B, or C): Allow the tool or workpiece to rotate in different directions.
This design enables the tool to access almost any surface of the workpiece. For example, when machining a complex blade, the tool can rotate around the curved surface, accomplishing tasks that traditional 3-axis machines simply can’t.
Advantages of 5-Axis Machining:
- Fewer setups and re-clamping
- Higher machining accuracy
- Efficient processing of complex surfaces
Main Types of 5-Axis CNC Machines
5-axis machines come in various forms, tailored to different structural and application needs:
- Trunnion Type: Rotational axes at the end of the spindle; ideal for small, complex parts.
- Swivel Head Type: The tool head rotates, offering high flexibility.
- Moving Column Type: The machine column moves, suitable for large workpieces.
- Table Type: The workpiece is fixed on a rotary table, ideal for medium and small parts.
- Head-Table Type: Both the spindle and table rotate, enabling complex machining.
- Continuous Type: Designed for mass production.
- Indexing Type: Used for precise indexing operations.
- Gantry Type: Highly rigid structure for large parts.
- Hybrid Type: Combines multiple structural advantages for special needs.
Each type has unique strengths. Choose according to your machining requirements and workpiece characteristics.
Core Advantages
Why are more and more manufacturers choosing 5-axis machines? The reasons are clear:
- Single Setup, Multi-Face Machining: Reduces repeated clamping and avoids cumulative errors.
- Improved Precision and Surface Quality: Flexible tool angles ensure more stable cutting.
- Shorter Production Cycles: Dramatically reduces machining time for complex parts.
- Lower Production Costs: Less manual intervention and fewer reworks.
- Meets Demands for Complex Parts: Perfect for aerospace, medical devices, and other high-end manufacturing.
Key Points for Selecting and Purchasing
| Key Technical Parameters | Configuration Options | After-Sales Service |
|---|---|---|
| Travel range (X, Y, Z axes) | CNC system brand (e.g., FANUC, Siemens) | Warranty and technical support |
| Spindle speed and power | Automatic tool changer and tool magazine | Response time for repairs |
| Machine repeatability and accuracy | Cooling system and protective devices | Training services |
Differences Between 5-Axis CNC Machines and 5-Face Machining Centers
| Item | 5-Axis CNC Machine | 5-Face Machining Center |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tool and workpiece can rotate simultaneously on two axes for complex surfaces | Usually a 3-axis machine with a rotary table, can machine five faces |
| Axis Motion | X, Y, Z linear axes + two rotational axes | X, Y, Z linear axes + one rotary table |
| Capability | Complex surfaces and high-precision machining | Multi-face flat or simple surface machining |
| Applications | High-precision, complex part machining | Multi-face flat or simple surface machining |
Typical Application Fields
The applications of 5-axis machines are broad, especially in these industries:
- Aerospace: Engine blades, structural parts, turbine blades, etc.
- Automotive: Engine components, molds, body structures.
- Mold Making: Complex surface molds, injection molds.
- Medical Devices: Artificial joints, orthopedic implants.
- Energy Equipment: Wind turbine blades, nuclear power components.
These fields demand high precision and complexity, making 5-axis machines the perfect solution.
Operation Process of 5-Axis CNC Machines
Operating a 5-axis machine isn’t magic-it’s a systematic process:
- CAD/CAM Modeling and Programming
Designers create part models in CAD software and generate tool paths and G-code using CAM software. - Workpiece Clamping and Tool Setting
The workpiece is fixed on the machine, ensuring accurate positioning. Tool setting ensures the correct relative position between tool and workpiece. - CNC System Controls Machining
The CNC system executes the program, and the machine follows the preset path to complete machining.
5-axis CNC machines are not only a technological powerhouse in modern manufacturing but also the key to efficient, high-precision machining. After reading this article, you should have a comprehensive understanding of their structure, principles, types, advantages, and applications.
If you’re considering upgrading your equipment or purchasing a 5-axis CNC machine for the first time, feel free to contact us. Our professional team will provide you with customized solutions to help your production reach new heights!
Don’t hesitate-take action now and let 5-axis CNC machines give wings to your manufacturing dreams! Click here to contact us for a quote and technical support.
FAQ
A 5-axis CNC lathe is a high-precision machine tool capable of machining along five different axes (usually X, Y, Z, A, and B or C) simultaneously. Compared to traditional 3-axis machines, 5-axis lathes allow for more complex part machining, improving efficiency and precision.
Multi-face machining in a single setup, reducing workpiece handling.
Enhanced capability for machining complex parts.
Improved machining accuracy and reduced cumulative errors.
Shorter production cycles and increased efficiency.
They are widely used in aerospace, automotive, medical, mold, and energy industries, suitable for machining complex surfaces, integral impellers, blades, propellers, and other high-precision parts.
Regularly calibrate the machine to maintain axis accuracy.
Use automatic measurement and calibration systems.
Enhance operator training for better programming and operation.
Simulate programs and check for potential collisions before production.





